Products - Inverters
See also: Quality and reliability | Environment
Description
Also so called inverter or ondulator, is an electronic circuit used to turn direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). The function of an inverter is to change the voltage of entry of direct current (it normally comes from a battery of 12 or 24 Vdc) to an alternate voltage of exit (normally tension of network (net) 110 or 230 Vac).
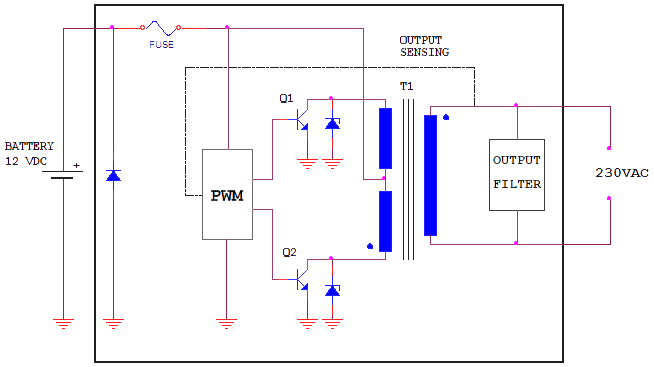
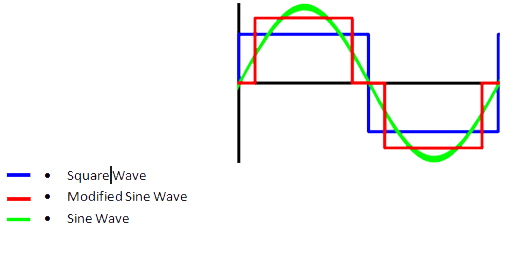
The inverters are in the habit of being composed of an oscillator that controls a transistor wich is used to interrupt the constant tension of entry and to generate a square wave. This square wave feeds a transformer that adapts the tension level wiched in the exit and a final filter smooth the waveform making it very similar to a pure sine wave. It is also possible to generate modified sine wave, wich is generated from three points: one positive, the negative one and one to ground. Modified since wave inverters can cause less efficiency especially when working with inductive loads.
Basic bloc diagram
Wave form
Parameters
- Output voltage.- It is the nominal voltage (Vac) that the inverter gives to make to work the equipments that connect.
- Output frequency.- It is the frequency (Hz) of the voltage of output.
- Power (continuous way).- Delivery supplies this power of an uninterrupted way
- Peak of Power.- Some equipments as, for example those who take an engine, they need an increase of power when being connected. Once the equipment is in a permanent way the consumed power is minor and can continue operating in constant way.
- Input voltage range.- It is the voltage variation of the source (battery) that the inverter admits to work; below the minimal voltage and over the maximum voltage the inverter will stop giving power.
- Protections.- Normally the following protections are in the habit of being incorporated:
- Protection of the variation of the tension of entry
- Protection against the overcharge of the output
- Overheating of the equipment
- THD (Total Harmonic Distorsion).- Of a signal, it is the measure of the harmonic present distortion in the signal and there is defined as the relation between the sum of the power of all the harmonic components and the power of the fundamental frequency.
- Efficiency.- Relation expressed in % between the power delivered in the output and the consumed power of entry.
-
Capacity of the batteries
- Voltage of the battery =
- Amperes/Hour =
- Consumed power =
- Proved Hours of functioning =
Working hours with Lead-Acid Battery
- Vbat(v) = Battery voltage = 12/24V
- Icap (Ah) = Battery capacity (aH) = it depends of the battery type, for instance = 90Ah
- K(%0) = Inverter efficiency aprox 70-85%
- P(W) = Total aplication power
- Pt(W) = Total power plus inverter efficiency
- Io(Ah) = Total current
- It(Ah) = Total current plus efficiency
- H(hours) = Working hours
- H=[Icap/It]
Example:
Having a lead-acid battery 12V/90Ah supplying a load in steady state of 500W the working ours will be:
- Vbat = 12V
- Icap = 90Ah
- P = 500W
- Pt = 650W
- Io = 41.66Ah
- It = 52.08Ah
- H=Icap/It=90/52.08=1.72 hours
Recommendations for better utilitzation
- Not to invert the polarity of the battery, the damages caused on the inverter can be irreversible.
- Not to use other cables a part from those given with the inverter.
- To leave one spread of at least 5cm in the overtures for the refrigeration of the inverter.
